Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a technology used by content creators and publishers to restrict access to their digital content. DRM is often used to protect copyrighted material such as music, movies, and software. However, the use of DRM has raised concerns about online privacy and the impact it has on the rights of individuals to access and use digital content.
The impact of DRM on online privacy is a complex issue that has been widely debated by scholars and experts in the field. On one hand, proponents of DRM argue that it is necessary to protect the intellectual property rights of content creators and publishers. They argue that without DRM, digital content would be vulnerable to piracy and illegal distribution, which would ultimately harm the creators and publishers of that content.
On the other hand, critics of DRM argue that it negatively impacts online privacy and individuals’ rights to access and use digital content. They argue that DRM restricts individuals’ ability to make fair use of digital content and can even prevent them from accessing content that they have legally purchased. Additionally, DRM can be used to collect personal information about individuals, which can be used for targeted advertising or other purposes that may be harmful to their privacy.
| Category | Statistic | Year |
|---|---|---|
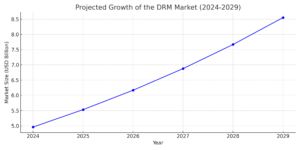
| DRM Market Size (Global) | USD 4.96 billion | 2024 |
| Expected Market Growth Rate (CAGR, 2024-2029) | 11.51% | – |
| Leading Region | North America | 2024 |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific | 2024-2029 |
| Key Market Segment by Application | Video-on-demand | – |
Digital Rights Management Fundamentals
Definition and Purpose of DRM
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a set of technologies, policies, and procedures that control access to digital content and protect the rights of copyright holders. The purpose of DRM is to prevent unauthorized access, copying, and distribution of digital content such as music, movies, and software, specifically designed to prevent users from violating copyright rules.
DRM is an essential tool for content creators and publishers to protect their digital assets and intellectual property rights from unauthorized users and to ensure that they are compensated for their work. DRM allows content creators to control how their work is used and distributed, which is critical for the success of the digital content industry.
DRM Systems and Technology
DRM systems encrypt and protect digital content using a combination of strong encryption techniques, digital signatures, watermarking, user authentication, and other technologies. Encryption scrambles the content so that it can only be accessed by authorized users. Digital signatures verify the authenticity of the content and ensure that it has not been tampered with.
DRM systems can be implemented in different ways depending on the type of content and the distribution model. For example, some DRM systems are integrated into digital media players such as iTunes, while others are implemented at the server level for online streaming services.
In conclusion, DRM is a critical tool for protecting the rights of copyright holders and ensuring the success of the digital content industry. By using encryption, digital signatures, and other technologies, DRM systems can control access to digital content and prevent unauthorized copying and distribution.
DRM’s Impact on Online Privacy

Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a technology used by content creators and publishers to protect their intellectual property from piracy and unauthorized distribution. While DRM has been effective in preventing piracy, it has also raised concerns about its impact on online privacy. This section will explore the impact of DRM on online privacy, including personal data and user privacy, privacy concerns with DRM, and DRM and data protection laws.
Personal Data and User Privacy
DRM often requires users to provide personal data to access content, such as their name, email address, and payment information. The content provider then stores this data, which can be used for marketing or other purposes. Users may be concerned about the collection and use of their personal data, especially if it is shared with third parties without their consent.
Privacy Concerns with DRM
DRM has been criticized for its potential to infringe on user privacy. For example, some DRM technologies may track user behavior or collect data about the user’s device without their knowledge or consent. This can include information about the user’s browsing history, location, and other sensitive data. This data can then be used to deliver targeted advertising or other marketing message.
DRM and Data Protection Laws
DRM must comply with data protection laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires companies to obtain user consent before collecting and using their personal data. DRM technologies must also ensure that user data is stored and processed securely and that users have the right to access, correct, or delete their data. Failure to comply with data protection laws can result in significant fines and legal penalties.
In conclusion, while DRM is an effective tool for protecting intellectual property, it must also be used responsibly and in compliance with data protection laws to ensure user privacy and data security. Content creators and publishers must be transparent about the data they collect and how it is used, and users must be informed about their rights and have the ability to control their personal data.
DRM in the Global Digital Economy
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a set of technologies and protocols that are used to protect digital content from unauthorized access and distribution. DRM has become an integral part of the global digital economy, where businesses use it to protect their intellectual property rights and ensure that they are compensated for their work. This section will explore the role of DRM in the digital economy, its impact on different industries, and international perspectives on its use.
Business Models and DRM
DRM has become an important part of many business models in the digital economy. For example, companies like Google use DRM to protect their software and services from piracy and unauthorized use. DRM is also used by content creators and distributors to protect their intellectual property rights and ensure that they are fairly compensated for their work.
DRM’s Role in the Music and Streaming Industry
DRM has had a significant impact on the music and streaming industry, including platforms like Twitch, where gaining visibility and even getting free Twitch followers is a common goal for many content creators. In the past, DRM was used to limit the number of devices that could use digital music files, restricting access to specific devices or platforms. However, this approach was unpopular with consumers and was eventually abandoned by most music services. Today, DRM is used to protect streaming services from unauthorized access and ensure that artists and rights holders are fairly compensated for their work.
International Perspectives on DRM
DRM has been a controversial topic in many countries around the world. In China, for example, the government has implemented strict DRM laws to protect the intellectual property rights of local businesses. However, some experts argue that these laws are too restrictive and may stifle innovation and creativity. In other countries, such as the United States and Europe, there is ongoing debate about the appropriate use of DRM and its impact on online privacy and consumer rights.
In conclusion, DRM has become an important part of the global digital economy, with many businesses relying on it to protect their intellectual property rights and ensure fair compensation for their work. However, its use remains controversial, with ongoing debate about its impact on online privacy and consumer rights.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
Digital Rights Management (DRM) has significant ethical and societal implications for online privacy. As technology continues to evolve, it is important to consider the impact of DRM on human rights, democracy, freedom of expression, inequality, and the Cambridge Analytica scandal.
Human Rights and Digital Privacy
DRM has the potential to infringe on human rights, especially the right to privacy. The use of DRM technologies can enable the tracking and monitoring of individuals’ online activities, which can lead to the collection and misuse of personal data. This can result in a violation of an individual’s right to privacy, which is a fundamental human right.
DRM’s Influence on Democracy and Freedom of Expression
DRM can also significantly impact democracy and freedom of expression. The use of DRM technologies can restrict individuals’ ability to access and share information online, which can limit their freedom of expression. This can have a significant impact on democracy, as it can limit individuals’ ability to participate in the democratic process.
The Cambridge Analytica scandal is an example of how DRM can be used to influence democracy. Cambridge Analytica used data from Facebook to target individuals with political ads, which had a significant impact on the 2016 U.S. presidential election. This highlights the need to consider the impact of DRM on democracy and freedom of expression.
In conclusion, the ethical and societal implications of DRM on online privacy are significant. It is important to consider the impact of DRM on human rights, democracy, freedom of expression, inequality, and the Cambridge Analytica scandal. As technology continues to evolve, it is important to ensure that DRM is used in a way that respects individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Video Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
How does DRM technology affect user privacy?
DRM technology can affect user privacy by collecting and processing personal data to enforce copyright protection. This can include information about the user’s device, location, and usage habits. While some DRM systems may claim to protect user privacy, others may use this data for targeted advertising or other purposes.
What are the implications of DRM on personal data security?
DRM can raise concerns about personal data security, as it requires the collection and storage of sensitive information. If this information is not properly secured, it can be vulnerable to data breaches and other forms of cyber attacks. Additionally, DRM systems may require users to provide personal information in order to access protected content, which can further compromise their privacy.
Can the implementation of DRM systems lead to privacy breaches?
Yes, the implementation of DRM systems can potentially lead to privacy breaches if they are not properly designed and implemented. For example, if a DRM system is hacked or otherwise compromised, it could expose sensitive user data to unauthorized parties. Additionally, if a DRM system is overly intrusive or collects too much data, it could put user privacy at risk.
What privacy concerns arise from the use of DRM by content providers?
Content providers may use DRM to restrict access to their content, which can limit user freedom and control over their own data. Additionally, some DRM systems may collect and use personal data for targeted advertising or other purposes, which can raise concerns about user privacy.
How do DRM practices intersect with digital privacy laws?
DRM practices can intersect with digital privacy laws in a variety of ways, depending on the specific laws and regulations in place. For example, some laws may require DRM systems to obtain explicit user consent before collecting or processing personal data. Other laws may require DRM systems to adhere to specific data security standards or provide users with greater control over their data.
In what ways can DRM solutions potentially infringe upon individual privacy rights?
DRM solutions can potentially infringe upon individual privacy rights by collecting and processing personal data without user consent or in violation of data protection laws. Additionally, DRM solutions may limit user control over their own data or restrict access to content in ways that infringe upon user freedom and privacy.